Connected smart devices and IoT applications are arguably the most influential technology that is powering the 2020s. Smart phones, connected cars, and IoT devices have completely shifted how we interact with the world. Previously offline industries, like critical infrastructure, have also begun adopting smart devices to move their operations into the future. The adoption and proliferation of connected devices, however, has created an expanded attack surface that has made us all more vulnerable to cyberattacks than ever.
In honor of National Cybersecurity Awareness Month 2023, we’ll look at how modern software development and testing is done for smart devices — from mobile phones to IoT hardware. A new frontier of security tools is empowering developers to take back control and get ahead of vulnerabilities found lurking in the software of the smart devices we rely on day in and day out.
By making continuous security testing a mainstay of mobile app and IoT device R&D, organizations can accelerate their software development processes and stay ahead of an evolving threat landscape. To achieve this, it’s time to move from the physical world to the virtual world. From developing and testing on physical devices to shifting to virtual devices that can natively run the same software. Gone are the days of racks on racks of physical phones or networking gear in device labs or cloud farms.
Security Penetration Testing
To perform thorough mobile AppSec and device firmware testing, developers and researchers need to test data at rest and in transit under real world and dynamic conditions. However, conducting these methods effectively is complex and challenging with physical devices. Their hardware and firmware are cumbersome to maintain and matrix test, slow down development cycles, and impede introspection across hardware, OS, app, data, and network layers.
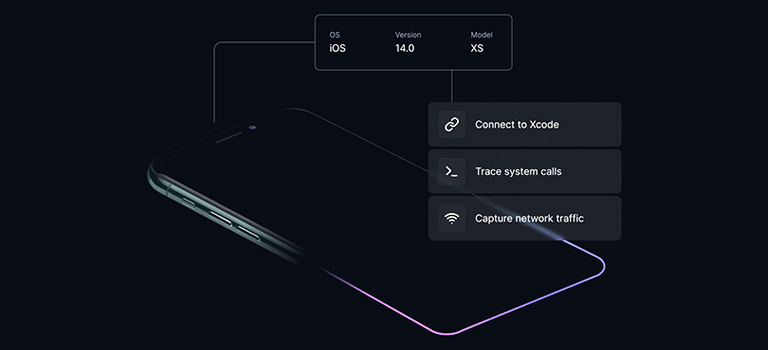
The recent advent of smart device virtualization, of iOS and Android phones to networking gear to automotive systems, has changed everything. The key to the innovation is the “Arm hypervisor.” Unlike servers and desktops that run on x86-based processors, nearly 95% of today’s smartphones, IoT devices, and automotive systems are powered by Arm-based processors. With Arm virtualization technology, developer teams can achieve Arm-native performance, accuracy, and device fidelity on virtual models of their physical counterparts.
These virtual models run production code, offer never-before-possible visibility and control, and drastically change the cost equation.
Arm virtualization platforms now include advanced tools that are purpose-built for developer and security testing teams:
- SAST (Static Application Security Testing): Through code review and static analysis, researchers scrutinize the source code of applications for vulnerabilities, backdoors, or obfuscated malicious code. This technique enables the identification of potential security weaknesses and malicious intentions. For iOS and Android devices in particular, virtualization enables direct root file system access to perform application static analysis and mobile forensics.
- DAST (Dynamic Application Security Testing): Dynamic analysis involves executing mobile applications or device firmware in controlled environments to observe their runtime behavior. Using virtualization, security and development teams have access to execution-level processes and memory and network monitoring tools that allow for real time analysis of application traffic.
Mobile Malware & Threat Research

Malware and social-engineering threats such as phishing is a key theme of National Cybersecurity Awareness Month, and understandably so. Phishing for example is pervasive and affects most people on a day-to-day basis. It’s goal is to trick people into divulging sensitive information or downloading malware, adware, and even ransomware. Our inboxes are flooded with phishing emails, and phishing text messages are inescapably common.
Many people are in tune with this reality, but phishing techniques are becoming more complex particularly with the advent of generative artificial intelligence and machine learning. As these technologies take root, cybercriminals and scammers will be able to up the scope, speed, and complexity of attacks leading to more breaches and supply chain attacks.
In this context, it’s critical for software developers to be able to investigate malware and phishing attacks to better develop their own mobile apps and user experiences to mitigate vulnerabilities and for threat research teams to investigate and respond faster to threats to their internal networks.
Virtualization provides developer and security teams with several key techniques and benefits:
- Device Procurement: Equipping security and threat research teams with the ever-expanding variety of devices, models, and software versions they need for adequate test coverage is a huge and costly challenge. Whether it’s iOS and Android mobile devices or awaiting the latest IoT device releases from engineering, security teams are often waiting or spending a vast majority of their time in managing physical device labs.
Virtual devices, in contrast, can be spun up on-demand with the OS and app versions needed for comprehensive and faster matrix testing.
- Secure Sandboxing:Virtualization provides isolated environments known as sandboxes. Within a sandbox environment, security teams can run untrusted applications without affecting the underlying system or other applications. Containment prevents the unauthorized access of sensitive data or other applications in the host system when conducting analysis and testing of suspected attacks.
- IOC Gathering & Threat Hunting: Researchers can augment static analysis with dynamic analysis by detonating malware or actively engaging with email attachment and smishing scams directly from a virtual iOS or Android device. This greatly improves the ability to uncover IOC (indicators of compromise) evidence and identify suspect vulnerabilities and active exploits.
- Source & Location Tracking: App debugging, file system, and SSL/TLS-stripped network monitoring tools help researchers identify sender sources and origin and destination IP addresses to better and more quickly evaluate suspected threats, from email attachments to SMS links and by dynamically setting the GPS location of virtual devices, researchers can trigger and analyze location-based malware and threats.
- Snapshotting and Cloning: With virtualized devices teams can configure, replicate, pause, snapshot and clone devices at any time. Whether during malware execution phases or after a test run, teams can reset the virtual device to its original or last known-good snapshot and within seconds are ready to begin the next round of testing. Device snapshots also greatly facilitate cross-team sharing and collaboration and can provide audit trail and compliance tracking.
Shaping the Future of Development

National Cybersecurity Awareness Month is an important time each year to raise awareness of ways we can each be more secure on an individual level. This year, we also point to how we can raise awareness for new tools, strategies, and research techniques that developers have at their disposal to make security an intrinsic part of every device they touch and for security teams to have more efficient ways of testing these devices.
Device virtualization is a significant game changer in the fight for cybersecurity that gives an edge to developer and test teams, helping them shift security left further upstream to achieve DevSecOps for their smart device and application SDLC (software development life cycle) processes. On-demand access to needed virtual device models and operating systems through one browser or API infrastructure streamlines the R&D process. The net result is faster R&D, better security, and lower costs.
Smart devices are the new cybersecurity battlefront. Vulnerabilities lie within device software and mobile apps themselves, and exploitation by malware and threat actors is ever increasing. Those that choose to look to the future, use the latest technologies and tools available, and build what’s next will be the heroes of a safer connected world.
Anthony Ricco


Leave a Comment